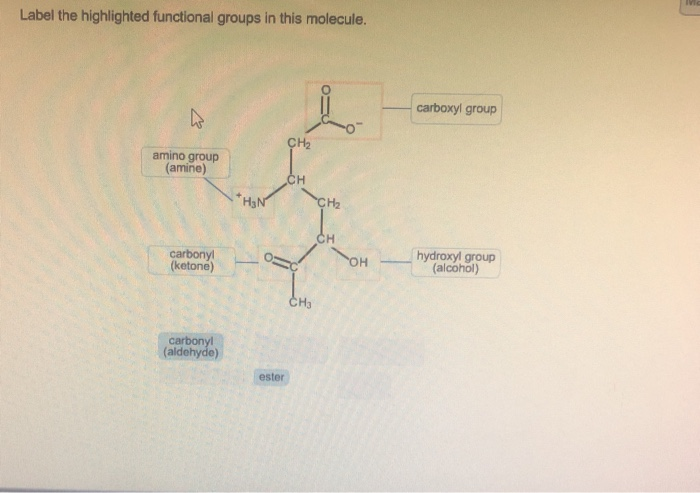
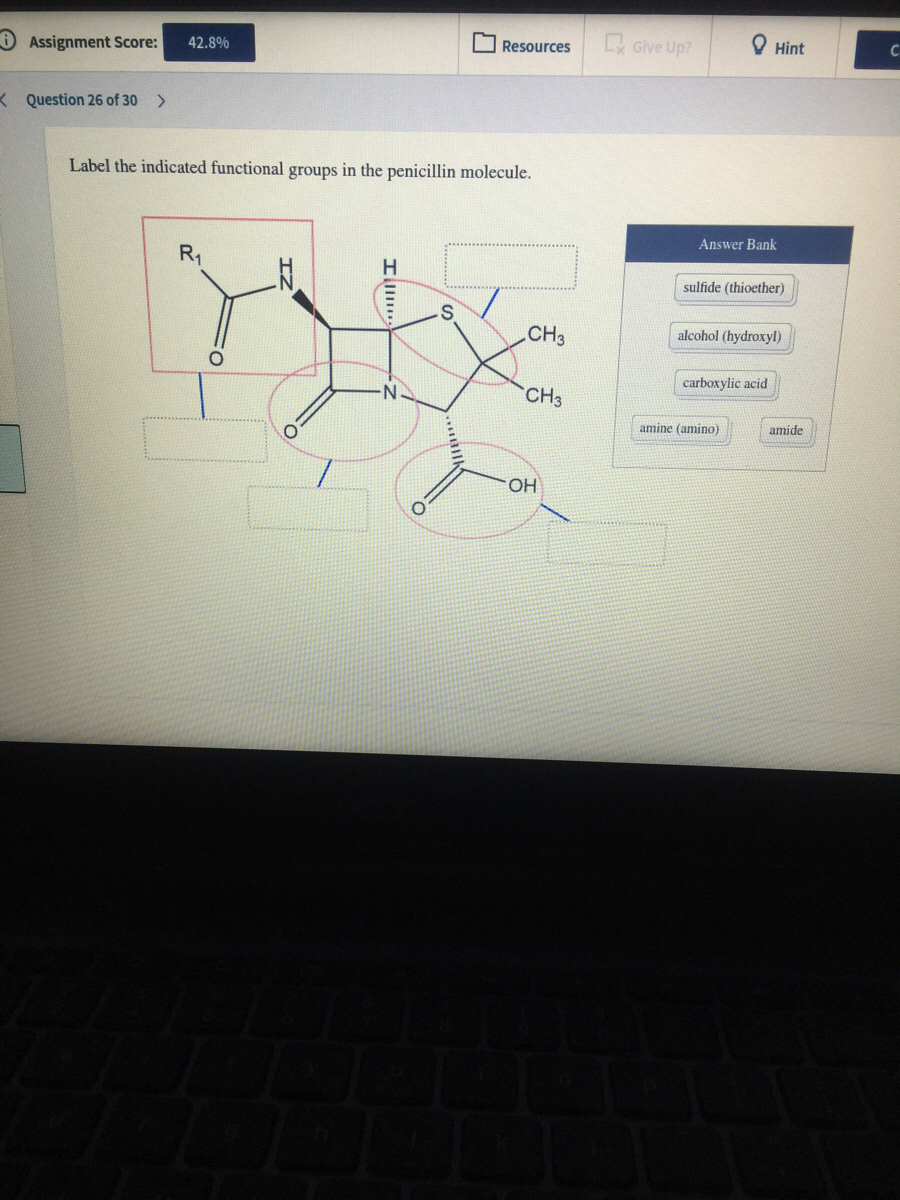
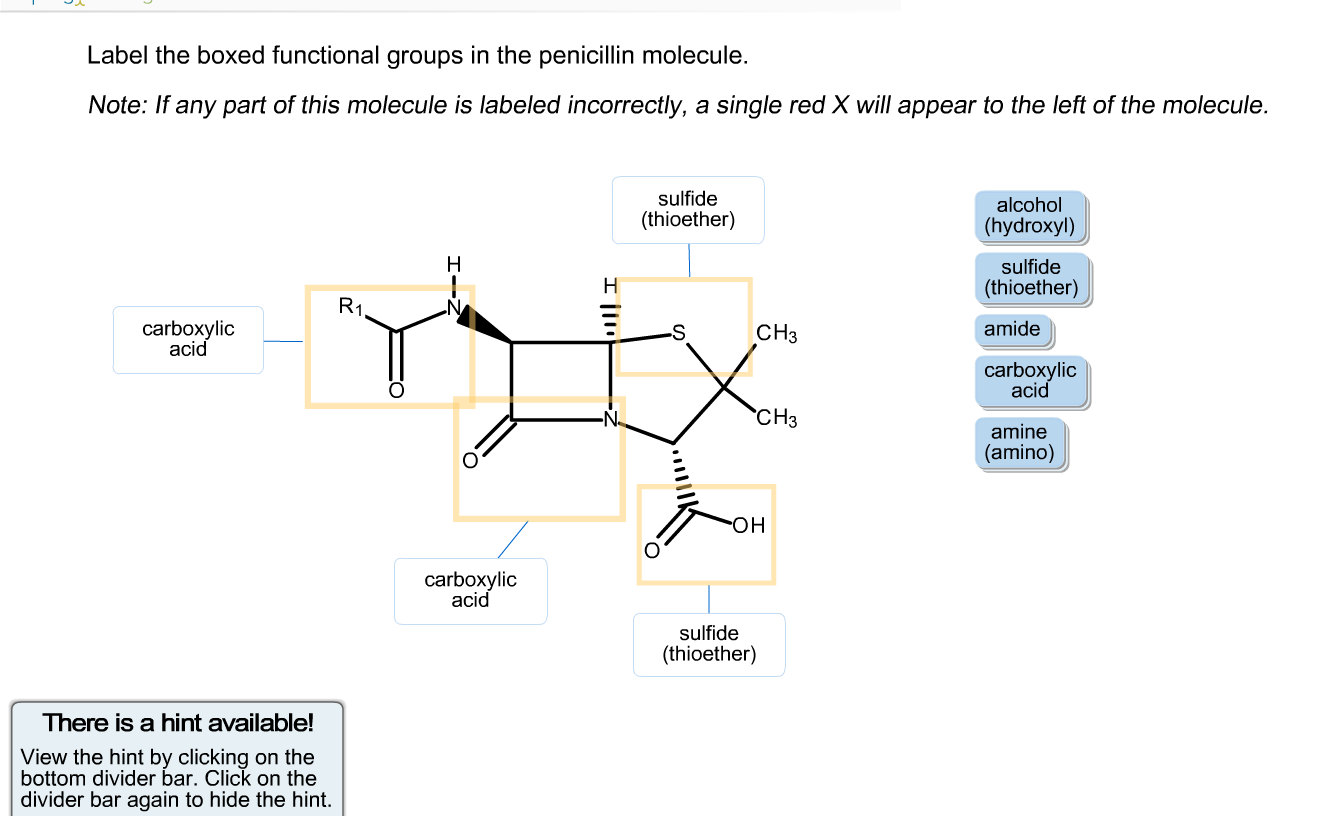
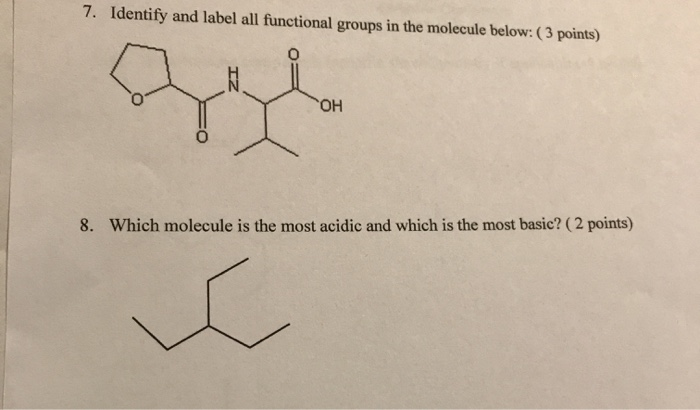
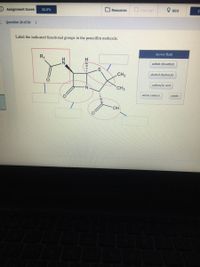
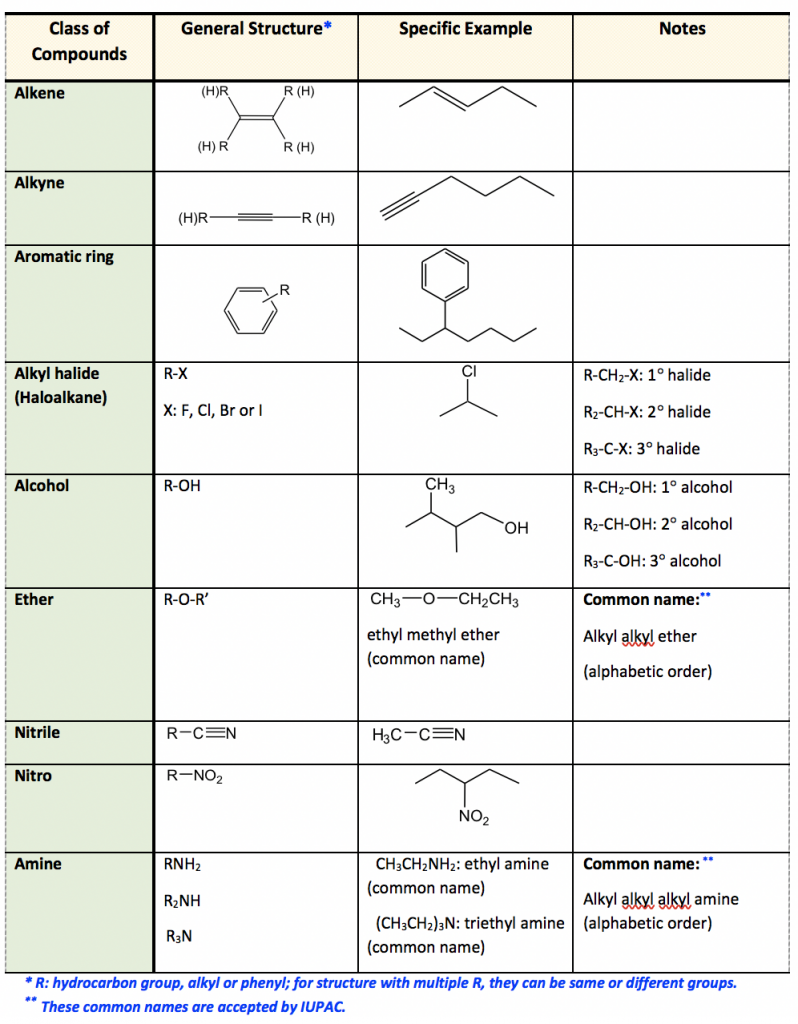
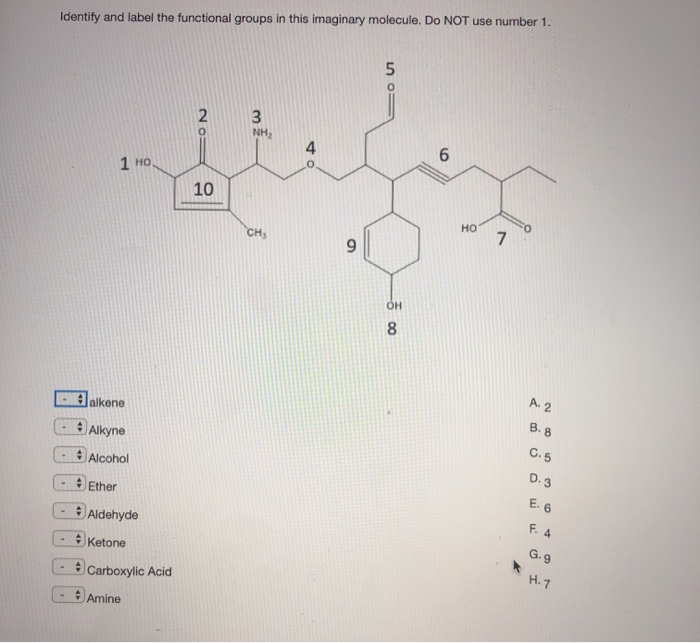
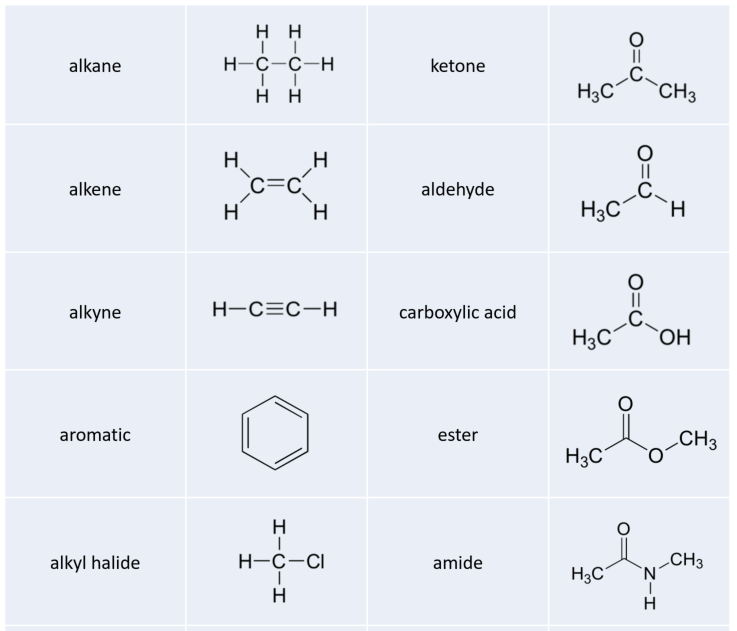
40 label the functional groups in the molecule
leah4sci.com › functional-group-priority-cheat-sheetFunctional Group Priority Chart - Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet Aug 08, 2016 · That's where this Functional Group Priority cheat sheet (scroll down) comes in. Find the highest priority group and make that your ‘functional group'. The lower priority groups get ‘demoted' to a substituent with regards to naming rules. See the individual naming tutorial videos for examples on how to name each functional group. Or start ... Acetals, Hemiacetals, Ketals & Hemiketals - Organic Chemistry Explained! Please note, while these two centers are Acetal and Ketal functional groups, they are also referred to as Anomeric Centers due to the fact that that are part of a carbohydrate molecule. For our purposes however, we will refer to the two Carbons using the Acetal and Ketal notations. Figure 3: Structure of Sucrose (Acetal and Ketal) Loading 3D model
atomicdesign.bradfrost.com › chapter-2Atomic Design Methodology | Atomic Design by Brad Frost In interfaces, molecules are relatively simple groups of UI elements functioning together as a unit. For example, a form label, search input, and button can join together to create a search form molecule. A search form molecule is composed of a label atom, input atom, and button atom. When combined, these abstract atoms suddenly have purpose.
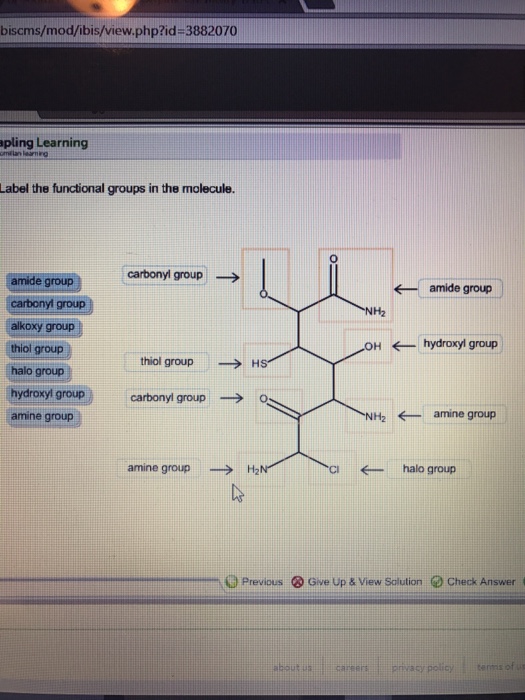
Label the functional groups in the molecule
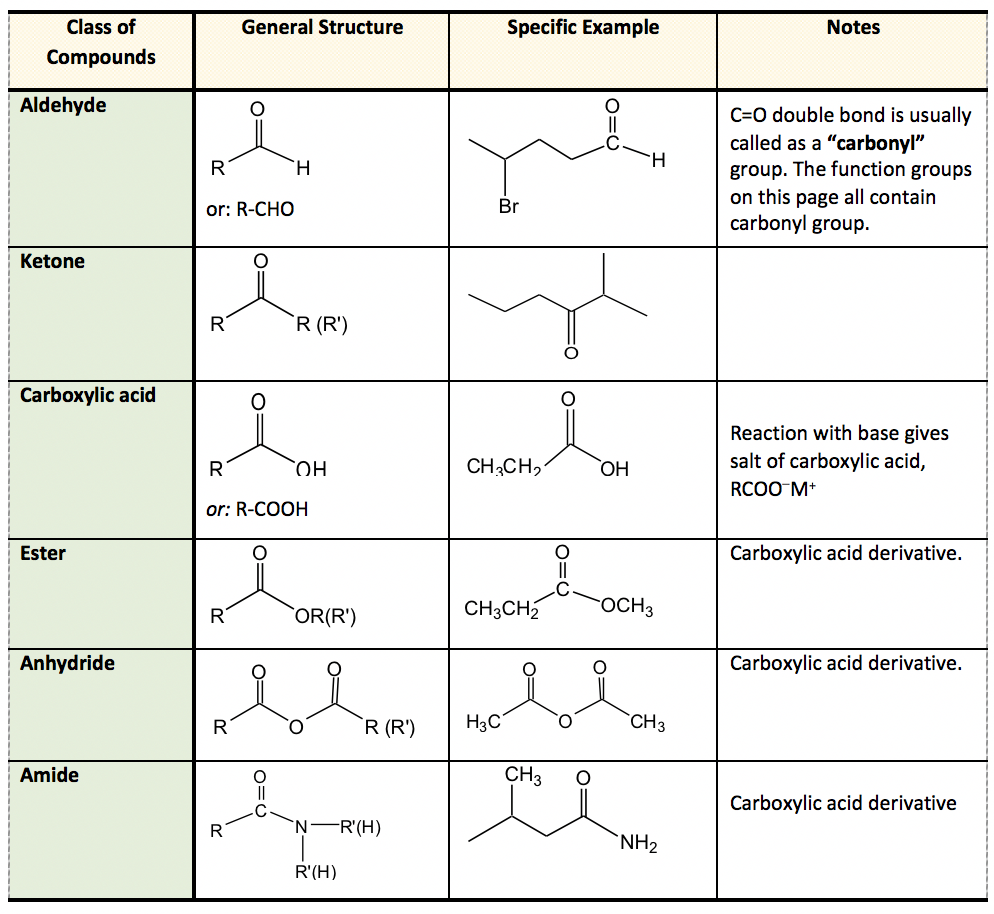
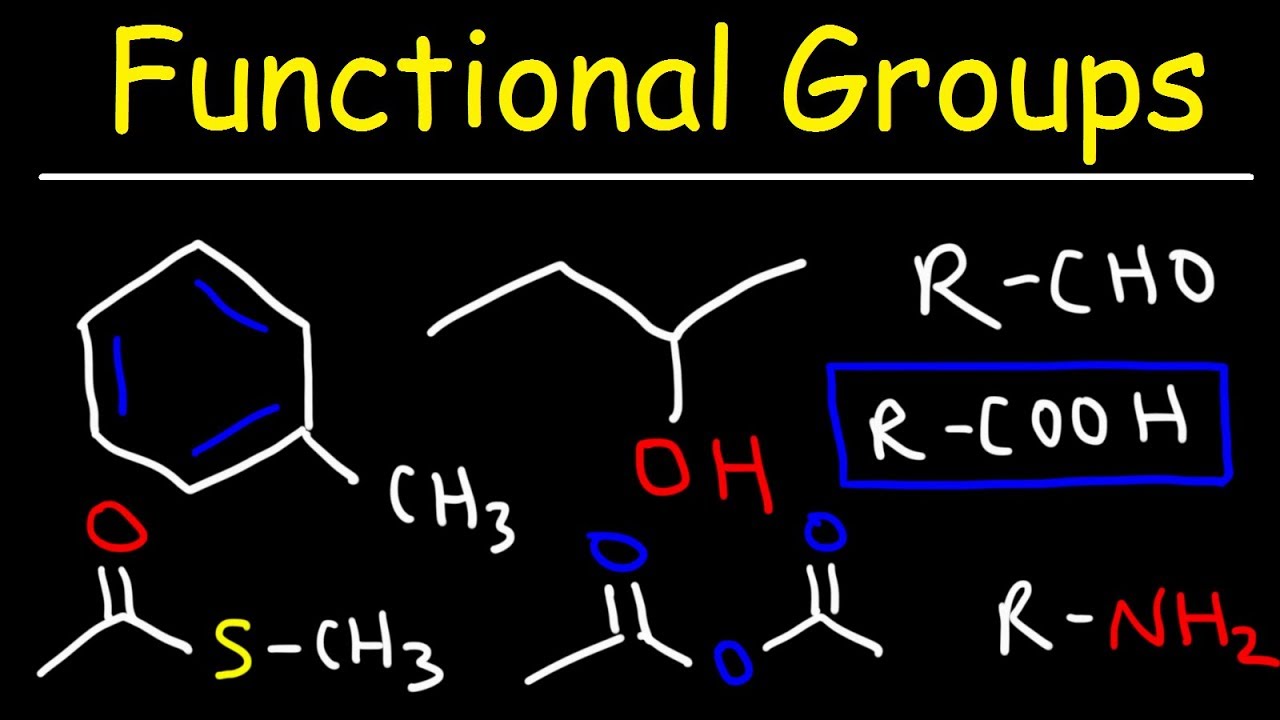
Carbonyl Functional Group | ChemTalk The carbonyl functional group is a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. The image below highlights (in red) the carbonyl group structure. The other two bonds coming off carbon (label R and R' in this case), can be any atom. The carbonyl part is just the carbon double bonded to oxygen (seen in red). en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Functional_groupFunctional group - Wikipedia The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a ... 3.1: Functional Groups - Chemistry LibreTexts Functional groups are small groups of atoms that exhibit a characteristic reactivity. A particular functional group will almost always display its distinctive chemical behavior when it is present in a compound. Because of their importance in understanding organic chemistry, functional groups have specific names that often carry over in the naming of individual compounds incorporating the groups.
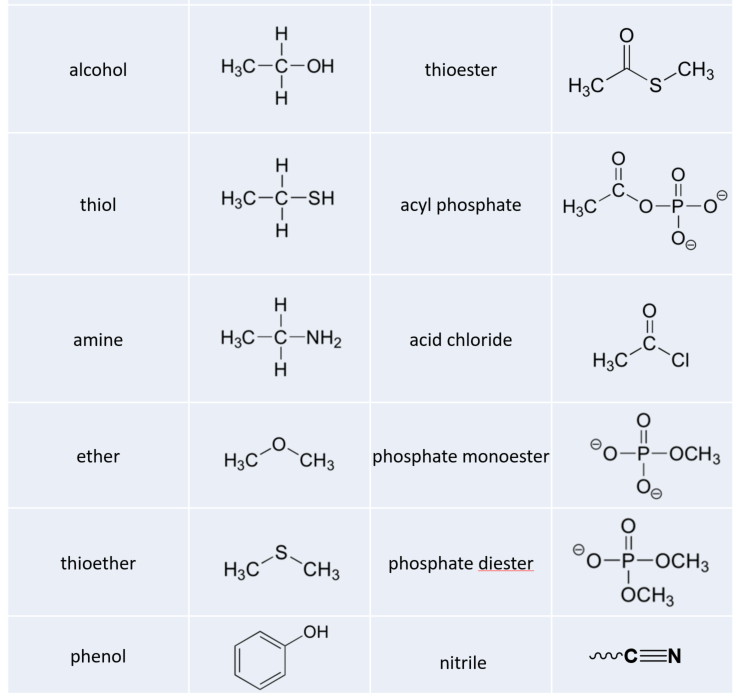
Label the functional groups in the molecule. › panoramic › indexPharmaCircle This website uses cookies to help provide you with the best possible online experience. Please read our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about ... EOF Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry | ChemTalk The hydrocarbon functional groups are alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons (arenes). Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups Groups containing oxygen may have a carbonyl (carbon-oxygen double bond) or not. The functional groups without carbonyls are ethers, alcohols, and epoxides. Organic Chemistry Functional Groups Guide + Cheat Sheet - Leah4sci To recognize this group in organic molecules, simply look for a line to F, Cl, Br, or I Naming Alkyl Halides Since halogens are substituents rather than functional groups, we include their name in the prefix. Take the full halogen's name, drop the ending and add 'o'. For example, iodine becomes 'iodo', chlorine becomes 'chloro'.
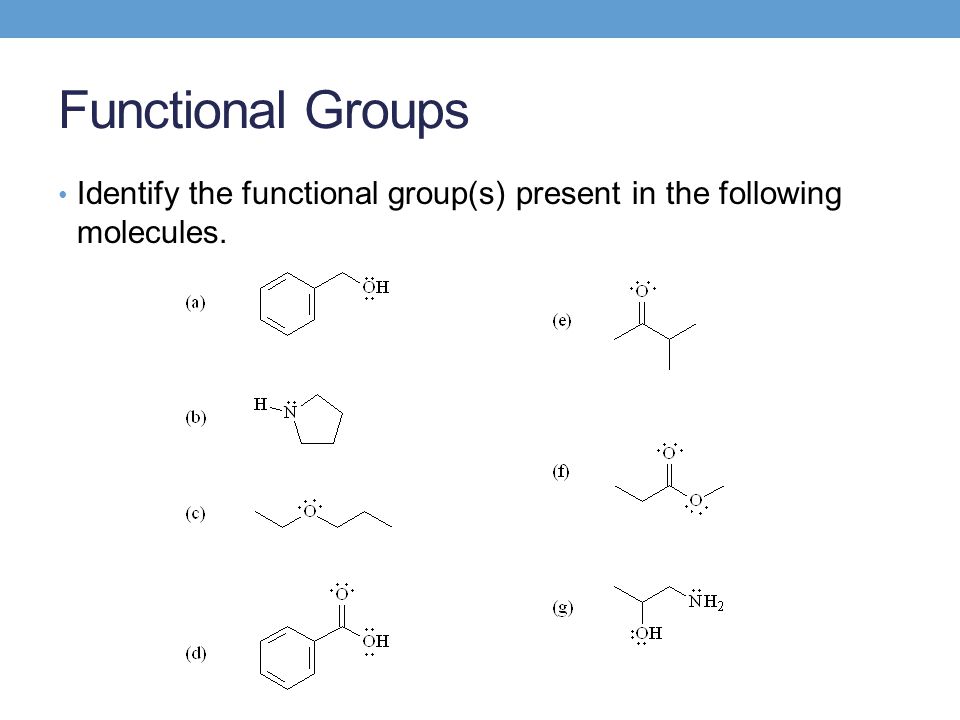
› our-therapy-areasCardiovascular, Renal and Metabolism (CVRM) - AstraZeneca Cardiovascular, Renal and Metabolism (CVRM) We have a relentless focus to further develop and deliver innovative, life-changing medicines and solutions for the millions of people affected by the complex spectrum of cardiovascular, renal and metabolism (CVRM) diseases. (Solved) - Identify the functional group(s) in the following compound ... (A) CH3NHCH3 AMINE FUNCTIONAL ... › questions-and-answers › prove-whyAnswered: Prove why the molecular identity of BF3… | bartleby typewritten Prove why the molecular identity of CF4 are the following: electronegativity difference of 1.5, polar bond, zero vector dipole moment, and non-polar molecule. Prove why the molecular identity of BF3 are the following: electronegativity difference of 2.0, polar bond, zero vector dipole moment, and non-polar molecule. (Get Answer) - Functional groups are the parts of organic molecules ... There are 7 functional groups for which you should know the structures. a) Draw the functional groups listed below and label each as polar/nonpolar. 1) Hydroxyl group 2) Carbonyl group 3) Carboxyl group 4) Amino group 5) Sulfhydryl group 6) Phosphate group 7) Methyl group b.
Draw And Label The Structure Of Dna And Rna - Bradley Cummerata Give general name for a carbohydrate molecule (i.e. Aug 13, 2020 · describe the structure and function of carbohydrates. Rna's role in the central dogma. Viruses vary in their structure. Find out how the dna code letters a, c, g, and t make a dna molecule by building one yourself. Identify functional groups of carbohydrates. Organic Molecule Overview & Examples | What is an Organic Molecule ... The atoms or groups of atoms that the carbon is bonded to give rise to the chemical characteristics of that compound. The group of atoms is called a functional group. Basic Functional Groups The... Photoredox-Catalyzed Decarboxylative C-Terminal Differentiation for ... To achieve successful labeling with any one method requires that the peptide fragments contain the functional group for which labeling chemistry is designed. In practice, only two functional groups are present in every peptide fragment regardless of the protein cleavage site, namely, an N -terminal amine and a C-terminal carboxylic acid. › article › academics-the-artsMolecules: Identifying Chiral Centers, Meso Compounds, and ... Dec 17, 2021 · Typically, you can only have diastereomers when the molecule has two or more chiral centers. The maximum number of possible stereoisomers that a molecule can have is a function of 2 n, where n is the number of chiral centers in the molecule. Therefore, a molecule with five chiral centers can have up to 2 5 or 32 possible stereoisomers! As the ...
Organic Chemistry: Test Your Knowledge About Functional Groups - ProProfs Functional groups are specific substituents within molecules responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional groups undergo the same reaction regardless of the size of their molecules. If you are a science student, you must have covered this topic in chemistry classes.
A deep-learning system bridging molecule structure and biomedical text ... Understanding molecule entities (i.e., their properties and interactions) is fundamental to most biomedical research areas. For instance, experts study the structural properties of protein ...
1.3: Functional groups and organic nomenclature University of Minnesota Morris. Functional groups are structural units within organic compounds that are defined by specific bonding arrangements between specific atoms. The structure of capsaicin, the compound discussed in the beginning of this chapter, incorporates several functional groups, labeled in the figure below and explained ...
CHE 120 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry - Textbook The amino acids found in proteins are L-amino acids. Exercises 1. Write the side chain of each amino acid. a. serine b. arginine c. phenylalanine 2. Write the side chain of each amino acid. a. aspartic acid b. methionine c. valine 3. Draw the structure for each amino acid. a. alanine b. cysteine c. histidine 4.
3.1: Functional Groups - Chemistry LibreTexts Functional groups are small groups of atoms that exhibit a characteristic reactivity. A particular functional group will almost always display its distinctive chemical behavior when it is present in a compound. Because of their importance in understanding organic chemistry, functional groups have specific names that often carry over in the naming of individual compounds incorporating the groups.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Functional_groupFunctional group - Wikipedia The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a ...
Carbonyl Functional Group | ChemTalk The carbonyl functional group is a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. The image below highlights (in red) the carbonyl group structure. The other two bonds coming off carbon (label R and R' in this case), can be any atom. The carbonyl part is just the carbon double bonded to oxygen (seen in red).

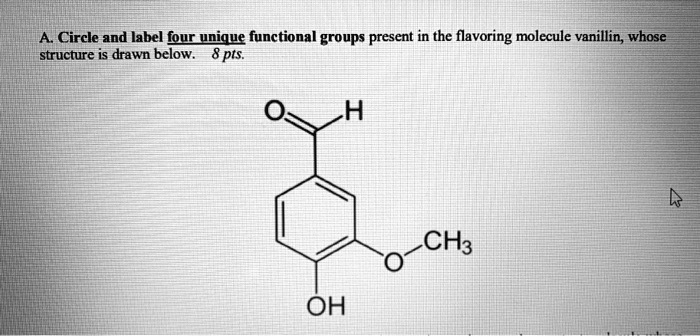


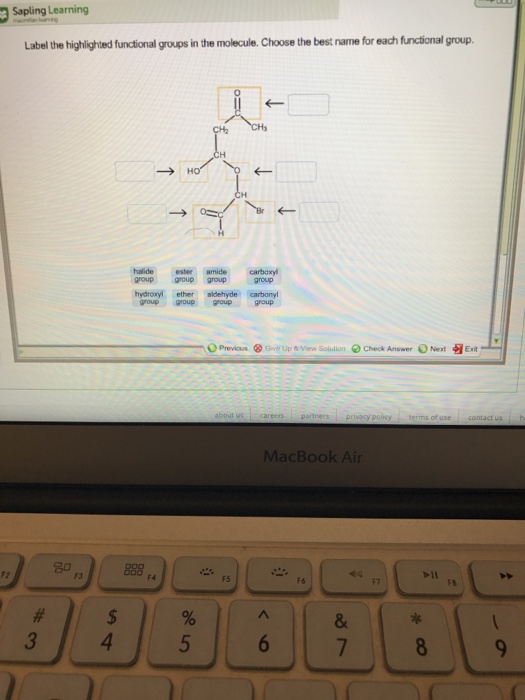
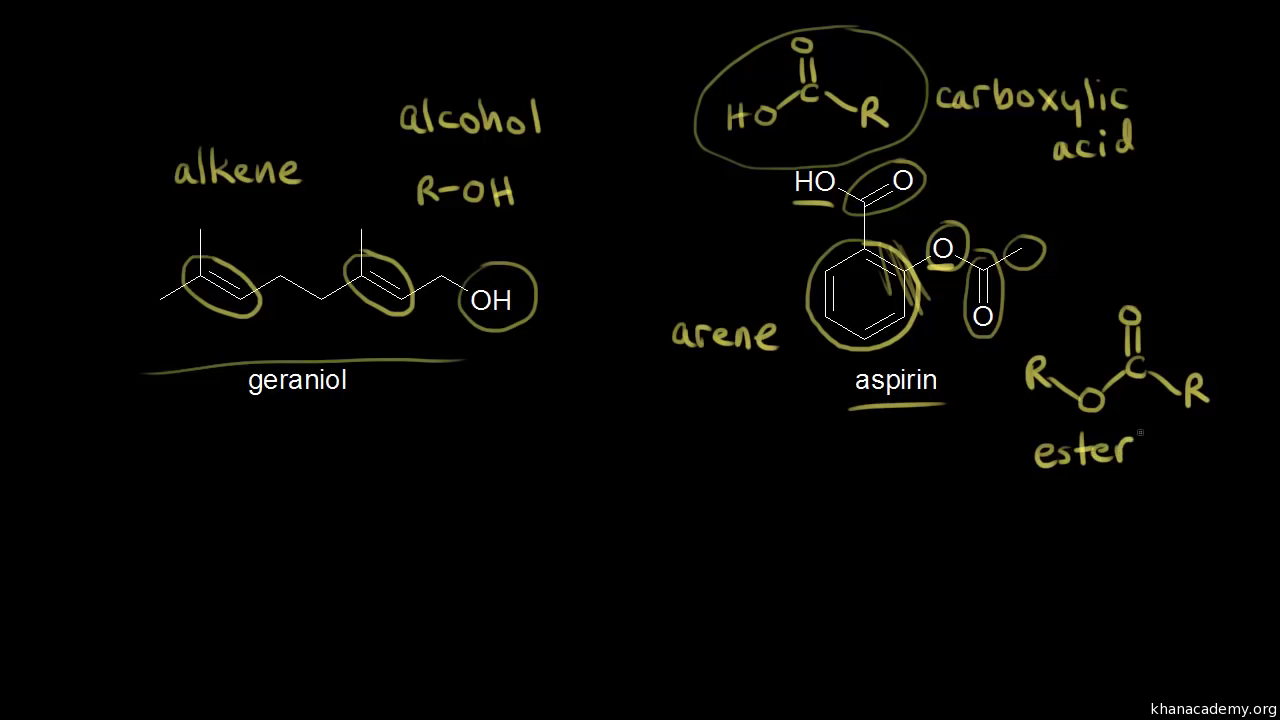






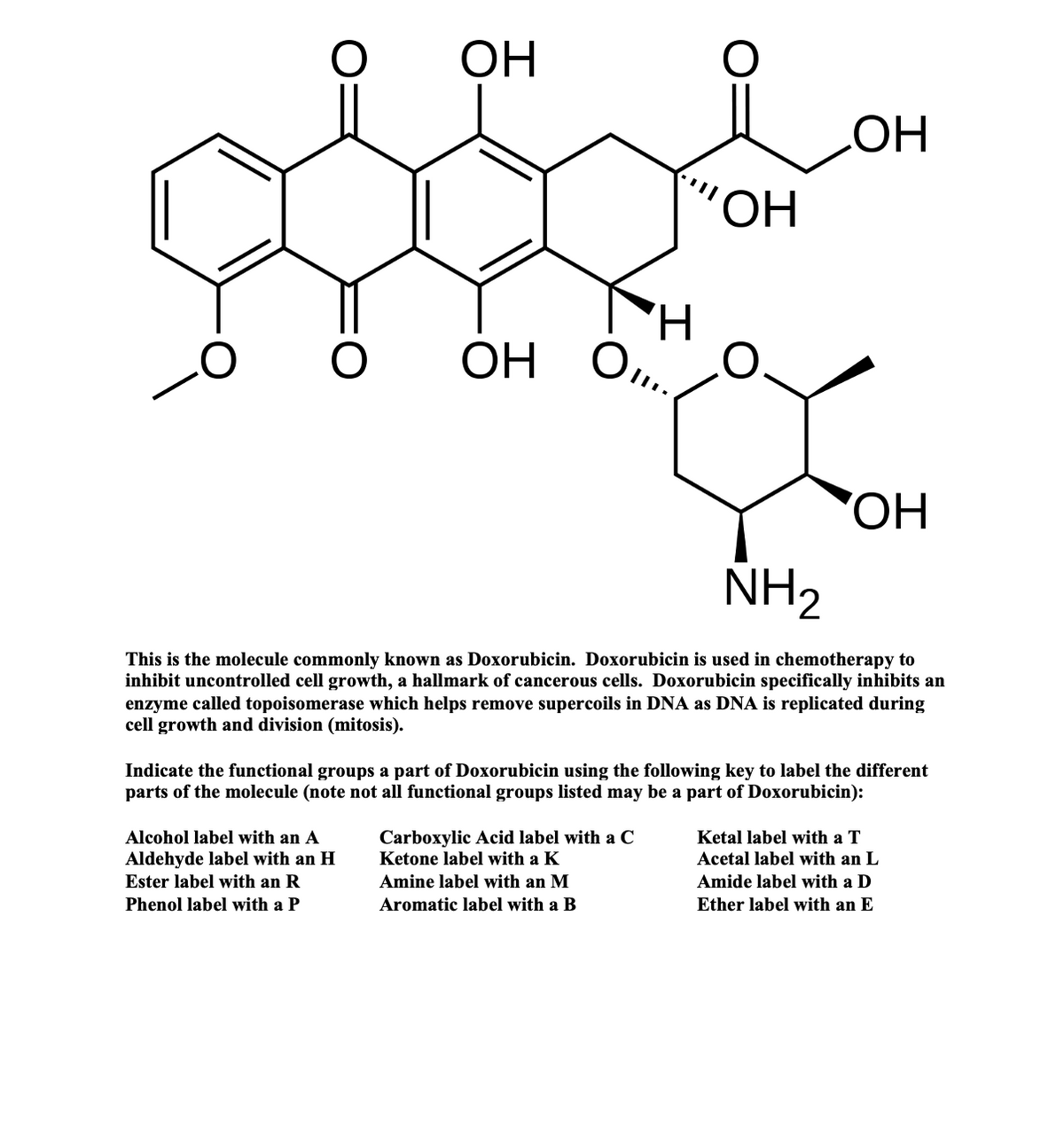
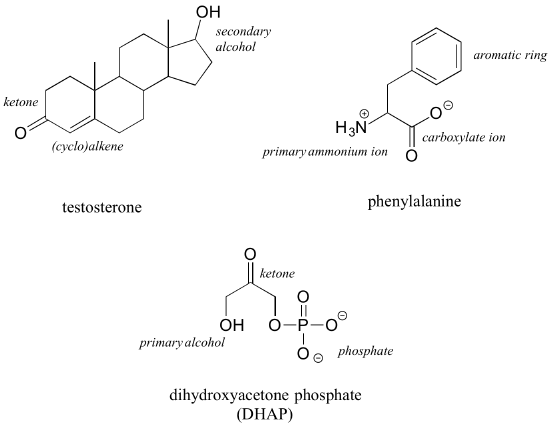
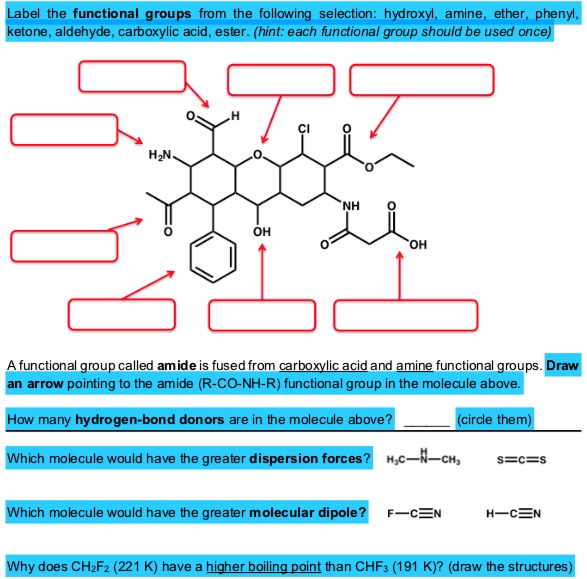
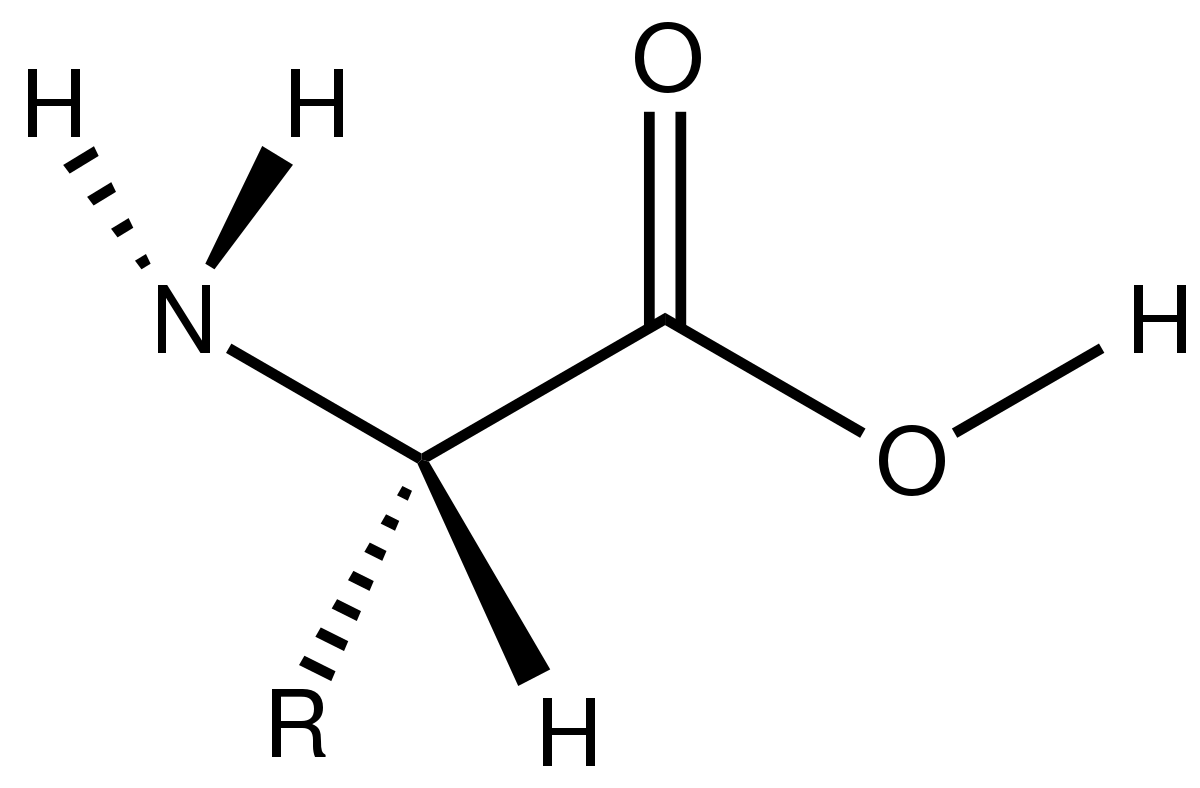








Post a Comment for "40 label the functional groups in the molecule"