39 label each part of the atp molecule
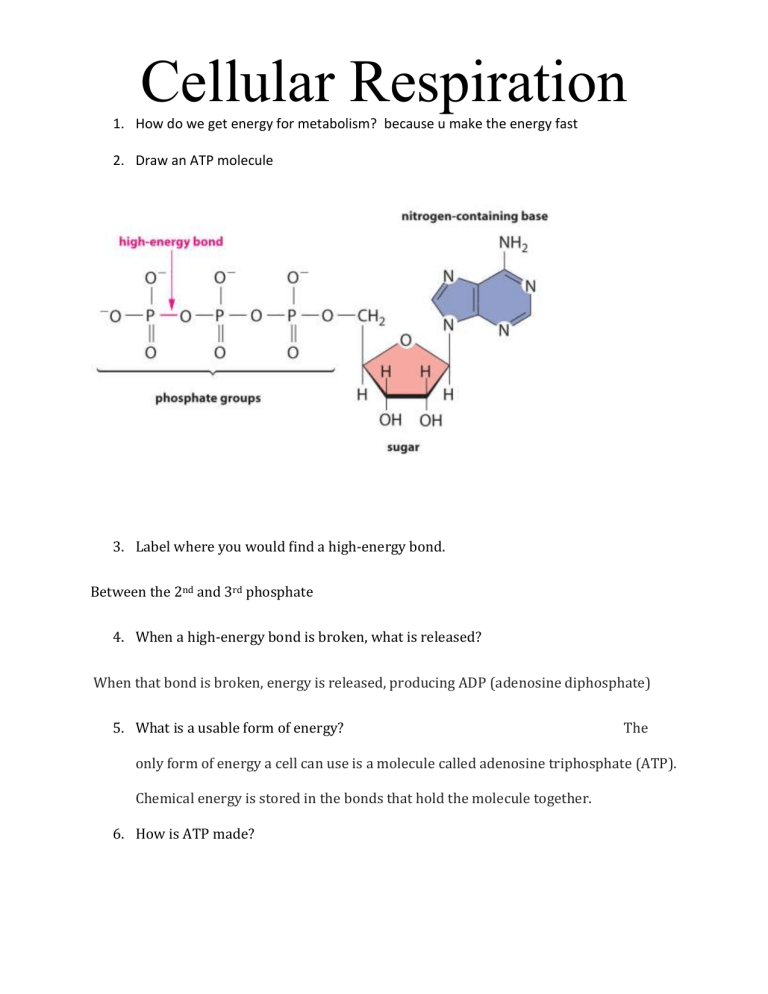
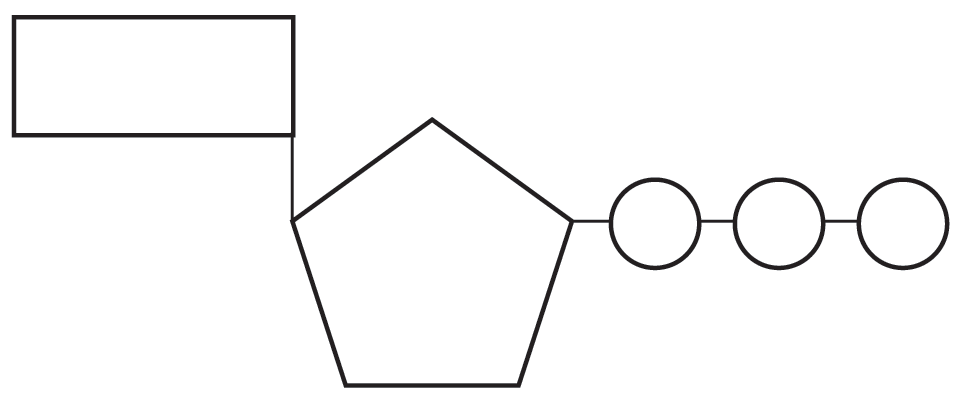
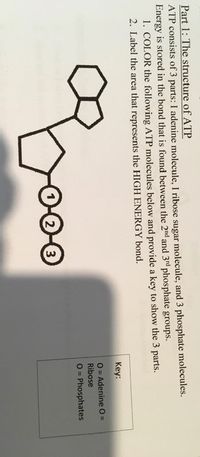
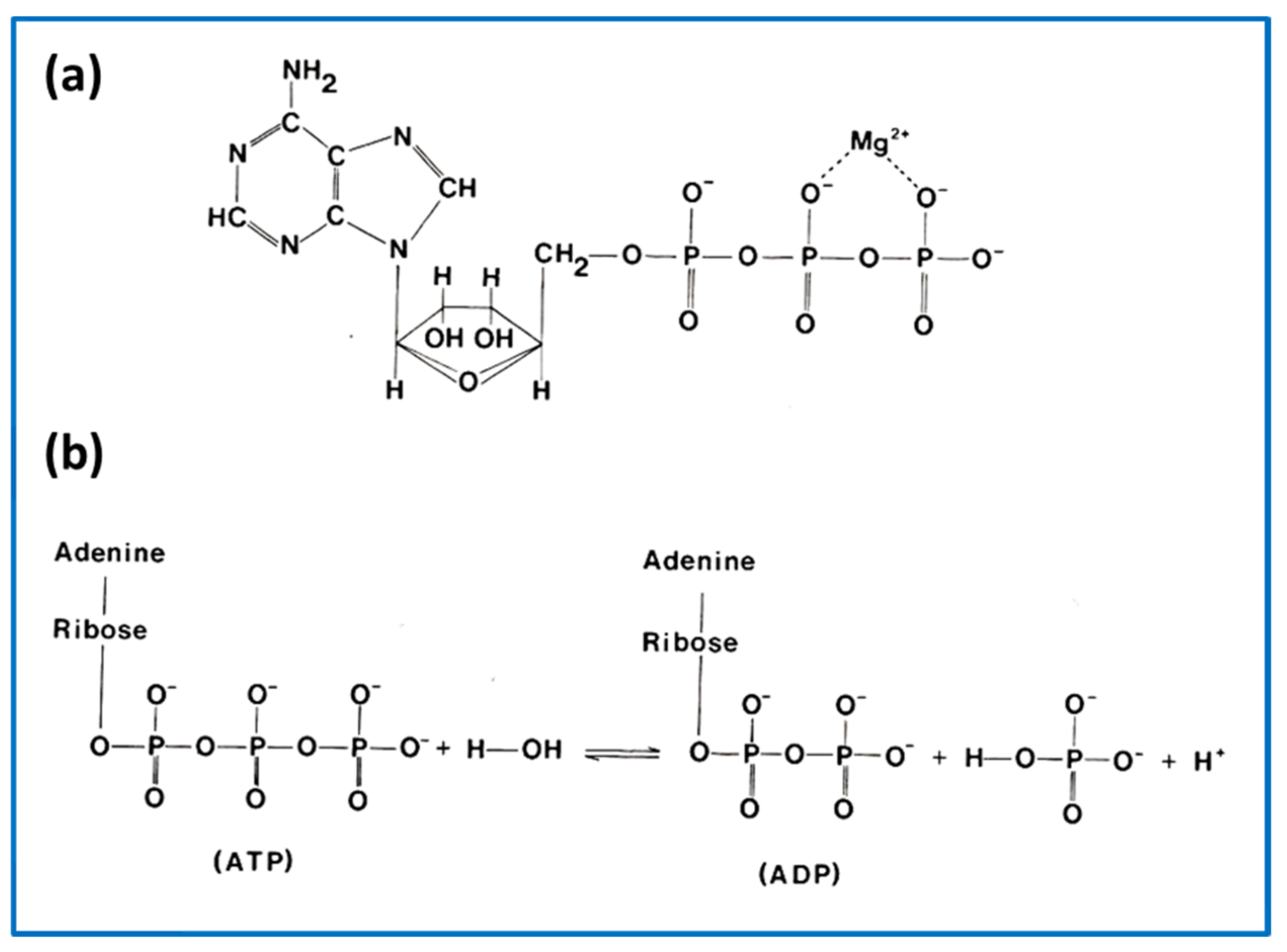
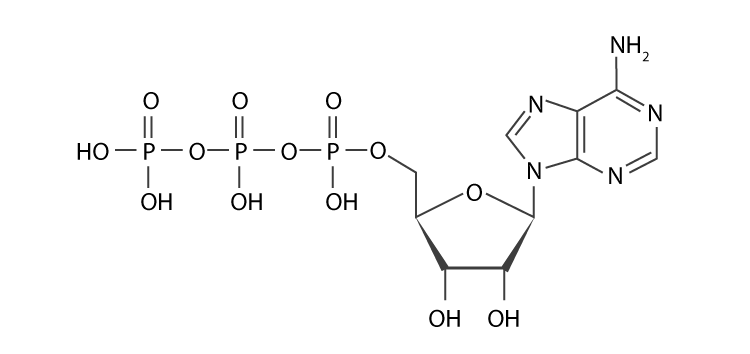
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. In the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the FANCM-family DNA helicase FmI1 directs NCO recombination formation during meiosis. u Based on these helicase motifs, a number of helicase superfamilies have been distinguished. In: Spies, M. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, TE - Scarsdale Public Schools Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples
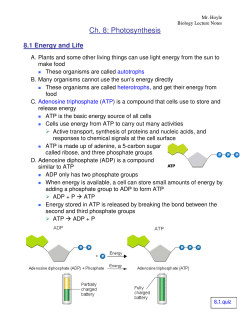
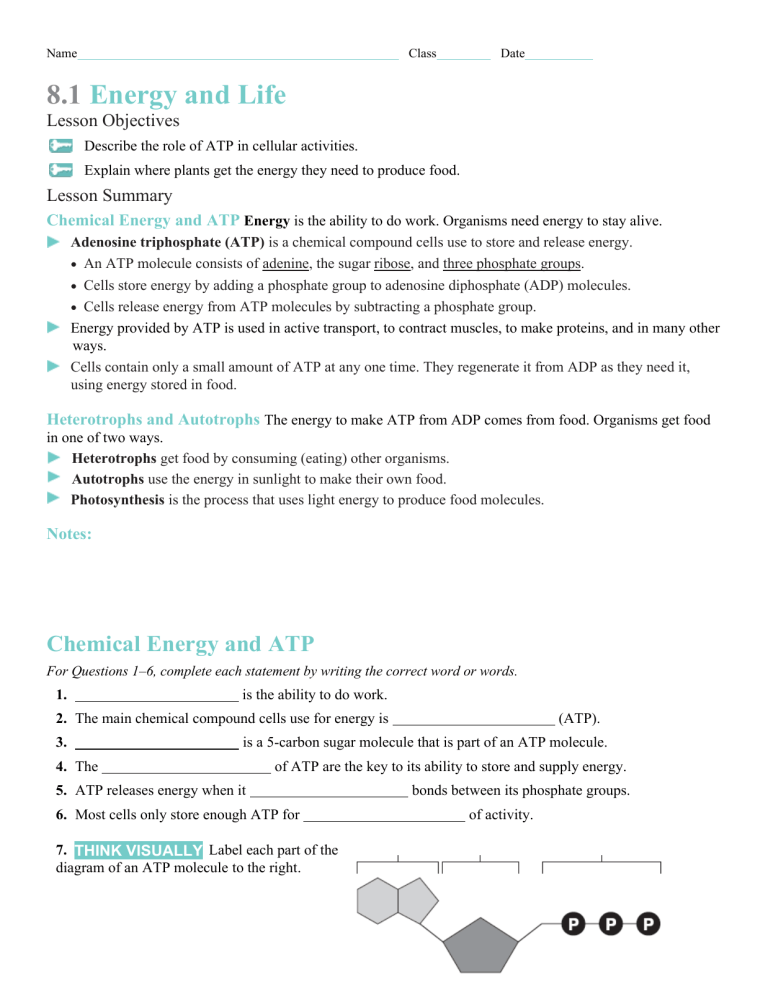
DOC 013368718X_CH08_115-128.indd - tesd.net ATP releases energy when it breaks . bonds between its phosphate groups. Most cells only store enough ATP for a few seconds . of activity. Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions 8-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low ...
Label each part of the atp molecule
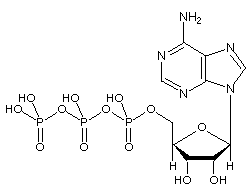
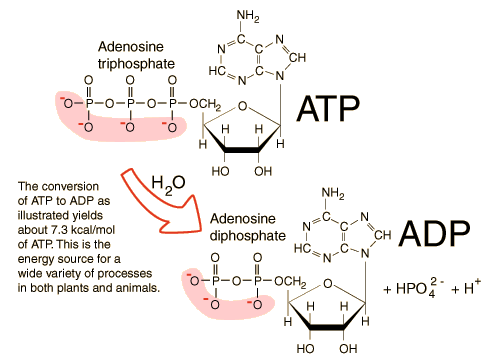
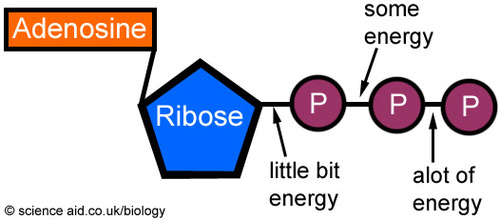
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) 7. From left to right- Adenine - Ribose - Phosphate groups 8. The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) … View the full answer Biology - Page 109 - Google Books Result 2015 · EducationGlycolysis produces a net gain of ______ ATP molecules per molecule of ... Label each diagram of a stage of mitosis in an animal cell with the proper number ... What is the Structural Difference Between ATP and ADP ATP molecule is composed of a ribose, an adenosine, and three phosphate groups. The first phosphate molecule is referred to as the alpha phosphate group. The second is the beta while the third is the gamma phosphate group. The three phosphate molecules are linked through negatively-charged oxygen molecules.
Label each part of the atp molecule. biology honors: chapter 8 Flashcards | Quizlet H+ ions accumulate within the thylakoid space, the build up makes the stroma negatively charged, the difference in both charge and H+ ion concentration provides energy to make ATP, H+ ions cannot directly cross the thylakoid so the ATP synthase allows H+ ions to pass through it, H+ ions pass through ATP synthase and force it to rotate, while rotating ATP synthase binds ADP & a phosphate group ... Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams Cellular Respiration Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38*ATP. 10. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, " biological machines " also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work. Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the ... Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
DOCX Home - The Kenton County School District Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. (3pts) How is energy stored and released by ATP? (2pts) Stored - Released - ... Label the three parts of this picture. (4pts) Introduction: A pigment is a substance that absorbs and reflects light of particular wavelengths. For example, the yellow-green color of a leaf is due to a ... Copy of 3.2.6 ATP_ In Search of Energy (1).pdf - 3.2.6 ATP: In Search ... 3.2.6 ATP: In Search of Energy All About ATP Draw an ATP molecule. Color code & label each of the parts of the molecule. Upload the picture here. Draw and name the cellular structure that produces ATP. Write the chemical formula involved. Upload the picture here. (Read direction #3 in PLTW) ATP & ADP Draw & describe how/why ATP turns into ADP. ATP.docx - ATP\u2014The Free Energy Carrier How does the ATP molecule ... View ATP.docx from BIO 101 at Issaquah High School. ATP—The Free Energy Carrier How does the ATP molecule capture, store, and release energy? Why? A sporting goods store might accept a $100 bill Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
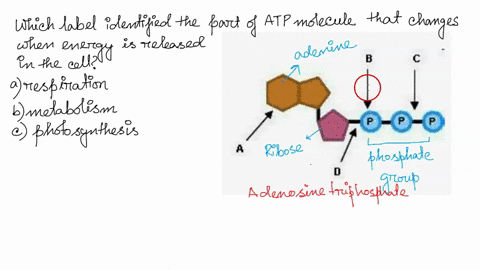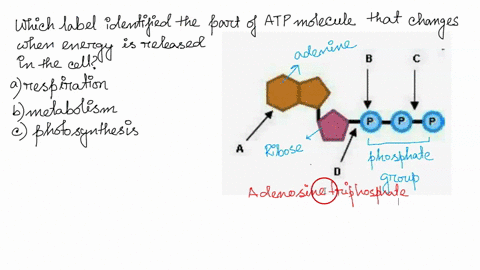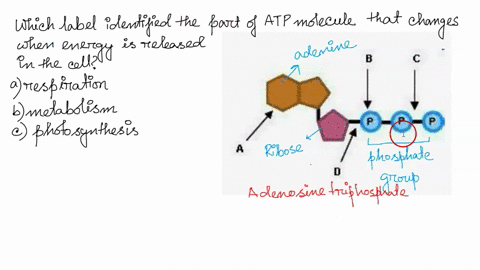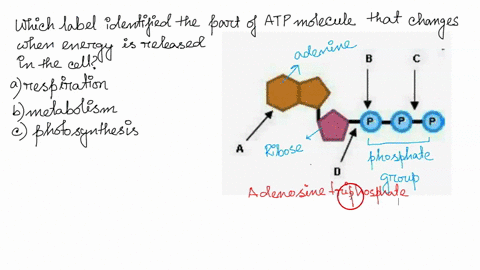
Photosynthesis: ATP and ADP Cycle - bealsscience ATP is one of the most important compounds inside a cell because it is the energy transport molecule. ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate) is considered a transporter of energy because when one of the phosphate groups is broken off, turning it into Adenosine DiPhosphate (the Tri means 3 phosphate groups, the Di means 2 phosphate groups). PDF AlP Formation - Mr. Mequi, Rangeview Science What is ATP an abbreviation for? 1. Label each part of the ATP molecule above in the spaces provided. 3. What is the sugar in ATP called? 4. How does ATP differ from ADP? 5. Explain how ATP is like a rechargeable battery. PART B In the space provided, draw and label the ATP Cycle. Include the following: ATP, ADP, phosphate, energy required ... PDF ATP - lcps.org List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c. A sporting goods store might accept a $100 bill for the purchase of a bicycle, but the Which label identifies the part of the atp molecule that changes when ... Label A; Respiration Explanation: Respiration identifies the part of the atp molecule that changes when energy is released in the cells of all living things. Hope this helps! Please mark brainliest! Advertisement Advertisement
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The ATP molecule is composed of three components. These phosphates are the key to the activity of ATP. ATP consists of a base, in this case adenine (red), a ribose (magenta) and a phosphate chain (blue). All living things, plants and animals, require a continual supply of energy in order to function.
ATP Overview & Uses | What Does ATP Stand For? - Study.com ATP definition: ATP is a high-energy molecule that can be found in all types of cells, including plant cells, muscle cells, nerve cells, and more. ATP is part of the larger macromolecule category ...
ATP Diagram | Quizlet a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di. two. ATP Cycle. a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP ... and Z) all found on one chromosome in Drosophila. Each gene has one dominant allele and one recessive allele. You perform the three different two-factor crosses (Cross 1: XY and ...
Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Explanation: Cellular respiration is the process by which nutrients such as glucose are broken down using oxygen to generate energy in the form of ATP, that is used to drive cellular processes. ATP consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups in a row. Energ Get more Answers for FREE
PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, SE - Loudoun County Public Schools Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P 6.
PDF Photosynthesis Study Guide - All-in-One High School Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released? ATP and Glucose 8. Circle the letter of molecules used to regenerate the energy in ATP. a.
PDF Scarsdale Public Schools / Overview Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups p p 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? It can add a phosphate group to ADP molecules, producing ATP molecules. 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released?
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
PDF AP BIOLOGY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES - College Board ATP and GTP are primary sources of energy for biochemical reactions. (a) Describe the structure of the ATP or the GTP molecule. (1 point each; 2 points maximum) • Adenosine + 3 phosphates or guanosine + 3 phosphates. • Elaborating on the phosphate bonds, e.g., unstable, negatively charged.
PDF ATP and Energy: How do cells capture, store, and release energy? 1. Based on the model of the ATP molecule above, list the three parts of the ATP molecule and then label each on the simplified model of ATP shown below a. b. c. 2. The full name for an ATP molecule is Adenosine Triphosphate. Based on the model for ATP, what is meant by the "tri" in triphosphate? 3.
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound and hydrotrope that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.
What is the Structural Difference Between ATP and ADP ATP molecule is composed of a ribose, an adenosine, and three phosphate groups. The first phosphate molecule is referred to as the alpha phosphate group. The second is the beta while the third is the gamma phosphate group. The three phosphate molecules are linked through negatively-charged oxygen molecules.
Biology - Page 109 - Google Books Result 2015 · EducationGlycolysis produces a net gain of ______ ATP molecules per molecule of ... Label each diagram of a stage of mitosis in an animal cell with the proper number ...
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) 7. From left to right- Adenine - Ribose - Phosphate groups 8. The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) … View the full answer



















Post a Comment for "39 label each part of the atp molecule"