44 prokaryote cell
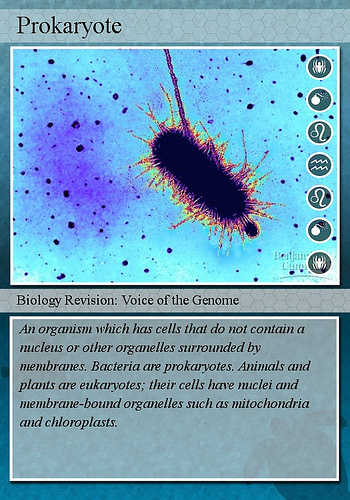
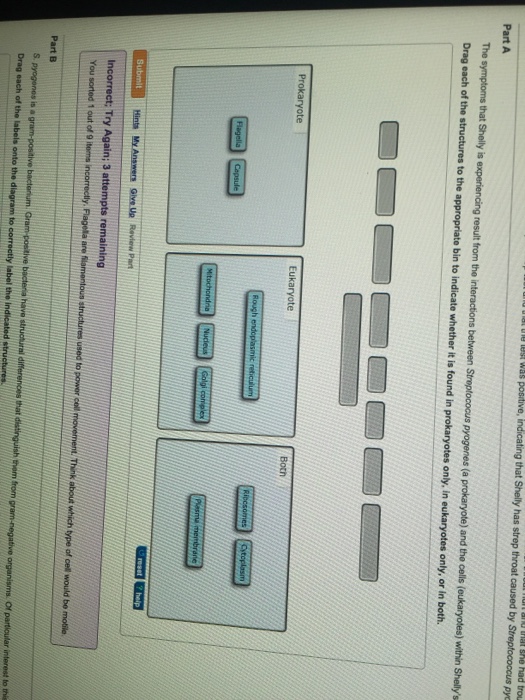
Prokaryotic Cell Definition - BYJUS Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis. A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane and therefore, all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm. Differences Between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell @ BYJU'S A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-bound cellular organelles. Prokaryotes are exclusively unicellular. What is a Eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles.
Cell Biology of Prokaryotic Organelles - PMC Abstract. Mounting evidence in recent years has challenged the dogma that prokaryotes are simple and undefined cells devoid of an organized subcellular architecture. In fact, proteins once thought to be the purely eukaryotic inventions, including relatives of actin and tubulin control prokaryotic cell shape, DNA segregation, and cytokinesis.

Prokaryote cell
Prokaryotes - Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells - Eduqas - GCSE Biology ... Prokaryotes Bacteria are amongst the simplest of organisms - they are made of single cells. Their cell structure is simpler than the cells of eukaryotes and cells are smaller, most are 0.2 μm - 2.0... The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? - Live Science The primarily single-celled organisms found in the Bacteria and Archaea domains are known as prokaryotes. These organisms are made of prokaryotic cells — the smallest, simplest and most ancient... Prokaryote's Bacteria Structure and Cell Capsule Function Introduction. A prokaryote is any organism whose genetic information is not enclosed within a membrane-bound nucleus. Prokaryotes may have one or many cells. They are genetically simpler than eukaryotes (usually have a membrane-bound nucleus) and have no membrane-bound organelles.They reproduce through cell division and consist of a single chromosome in a circular DNA molecule.
Prokaryote cell. Prokaryotic Cell: Definition, Functions, Diagram, Examples Prokaryotic cells are the unicellular cells that lack a well-defined nucleus, i.e. genetic material is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane. These cells are very minute in size \ (0.1\) to \ (5.0\, {\rm {\mu m}}\). Common prokaryotic cell is a bacterial cell. Our body has over \ (100\) trillion bacterial cells. Prokaryotic Cell - Structure, Types, Features and Reproduction A prokaryotic cell can be defined as a cell which does not have a well-defined nucleus or membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria or and lysosomes. An organism with a prokaryotic cell is called a prokaryote and they are generally bacterias. Although most bacteria cause diseases some are beneficial. The function of these prokaryotic cells ... Prokaryotic Cell - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics In primordial prokaryotic cells, families of transport proteins arose to serve a variety of cellular functions, including the regulation of cell pH and the provision of carbohydrate for cellular energy. Prokaryotic Cells: Structure, Function, and Definition Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that are the earliest and most primitive forms of life on earth. As organized in the Three Domain System, prokaryotes include bacteria and archaeans. Some prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, are photosynthetic organisms and are capable of photosynthesis .
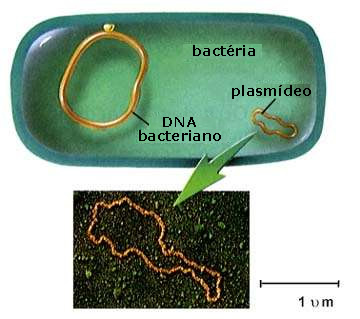
Prokaryotic cells (article) | Khan Academy Only the single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea are classified as prokaryotes— pro means before and kary means nucleus. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all eukaryotes— eu means true—and are made up of eukaryotic cells. Often, though—as in the case of we humans—there are some prokaryotic friends hanging around. Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell 3) Prokaryotic cell is a bacterium, while a eukaryotic cell is an organism consisting of many cells. 4) Prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells both in size and number. 5) Eukaryotes can turn into prokaryotes if conditions demand it to do so. This is called "bacterialisation". This is also known as "conversion" or ... Prokaryote - Wikipedia Diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell. A prokaryote ( / proʊˈkærioʊt, - ət /) is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό ( pro, 'before') and κάρυον ( karyon, 'nut' or 'kernel'). Prokaryotic cell | definition of prokaryotic cell by Medical dictionary prokaryotic cell The form of cell composing many primitive unicellular organisms, such as bacteria. Prokaryotic cells do not have nuclei, which are partitioned by an intracellular membrane; instead the DNA forms one main coil in the cell cytoplasm. See also: cell Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners prokaryotic cell
Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Prokaryotic Cells Components of Prokaryotic Cells. All cells share four common components: 1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; 2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like cytosol within the cell in which there are other cellular components; 3) DNA, the cell's genetic material; and 4 ... 71 Structure of Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea The Prokaryotic Cell. Recall that prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles or other internal membrane-bound structures (Figure 2). Their chromosome—usually single—consists of a piece of circular, double-stranded DNA located in an area of the cell called the nucleoid. Most prokaryotes have a cell wall outside ... Prokaryotic Cells - Brooklyn College Prokaryotic cells walls give structural integrity and shape to the cell and serve to anchor the whip-like flagellae (see below). A Plasma Membrane. Just inside the cell wall, the plasma membrane is a selective barrier which regulates the passage of materials to from the cell. It is through this membrane that a cell must exchange food molecules ... 4.2 Prokaryotic Cells - Biology | OpenStax Components of Prokaryotic Cells. All cells share four common components: 1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; 2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like cytosol within the cell in which other cellular components are found; 3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and 4 ...
Prokaryotic Vs. Eukaryotic Cells | Differences & Examples Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells are extremely small, much smaller than eukaryotic cells. A typical prokaryotic cell is of a size ranging from 0.1 microns 0.1 m i c r o n s ( mycoplasma bacteria) to 5.0 microns 5.0 m i c r o n s. 1 micron 1 m i c r o n or micrometer, μm μ m, is one-thousandth of a millimeter or one-millionth of a meter.
prokaryote | Definition, Example, & Facts | Britannica prokaryote, also spelled procaryote, any organism that lacks a distinct nucleus and other organelles due to the absence of internal membranes. Bacteria are among the best-known prokaryotic organisms. The lack of internal membranes in prokaryotes distinguishes them from eukaryotes. The prokaryotic cell membrane is made up of phospholipids and constitutes the cell's primary osmotic barrier.
Prokaryotic Cell - Definition, Examples & Structure | Biology Dictionary A prokaryotic cell is a type of cell that does not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Organisms within the domains Bacteria and Archaea are based on the prokaryotic cell, while all other forms of life are eukaryotic. However, organisms with prokaryotic cells are very abundant and make up much of Earth's biomass. Overview
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes - Visible Body Instead, their DNA is circular and can be found in a region called the nucleoid, which floats in the cytoplasm. Prokaryotes are organisms that consist of a single prokaryotic cell. Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They range from 10-100 μm in diameter, and their DNA is contained within a membrane-bound nucleus.
Prokaryotic Cells - Visible Body Prokaryotic cells are normally smaller than eukaryotic cells, with a typical size range of 0.1 to 5 μm in diameter. Prokaryotes are made up of a single cell, though they can pair up or cluster together to form mats. 2. Structures on the outside of a bacterium protect it and help it move
Prokaryotic Cells | Basic Biology Prokaryotic cells are tiny. They are about 10% as wide as the eukaryotic cells of plants, animals or fungi. The diameter of a prokaryotic cell is usually between 1-10 μm, whereas a typical eukaryotic cell is between 10-100 μm. The smallest bacteria, called mycoplasmas, can be as little as 0.1 μm in diameter.
Prokaryote - Definition and Examples | Biology Dictionary Prokaryotic cells are simple cells that do not have a true nucleus or other cell organelles. Bacteria and Archaea are the two domains of life that are prokaryotes. Prokaryotes can be contrasted with eukaryotes, which have more complex eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and organelles.
What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells? Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0.1-5.0 µm. Where do cells come from? All cells come from pre-existing cells by cell division. Schwann also proposed "Free Cell Formation" or spontaneous generation of cells — this was before Pasteur's definitive experiments. Modern Cell Theory Also States: Life's chemical processes, such as ...
Prokaryotic Cell - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Prokaryotic cells represent the smallest and simplest form of life that can metabolize, grow and reproduce. They are presumed to resemble the earliest forms of life and they reproduce much more quickly than multicellular organisms do.




Post a Comment for "44 prokaryote cell"